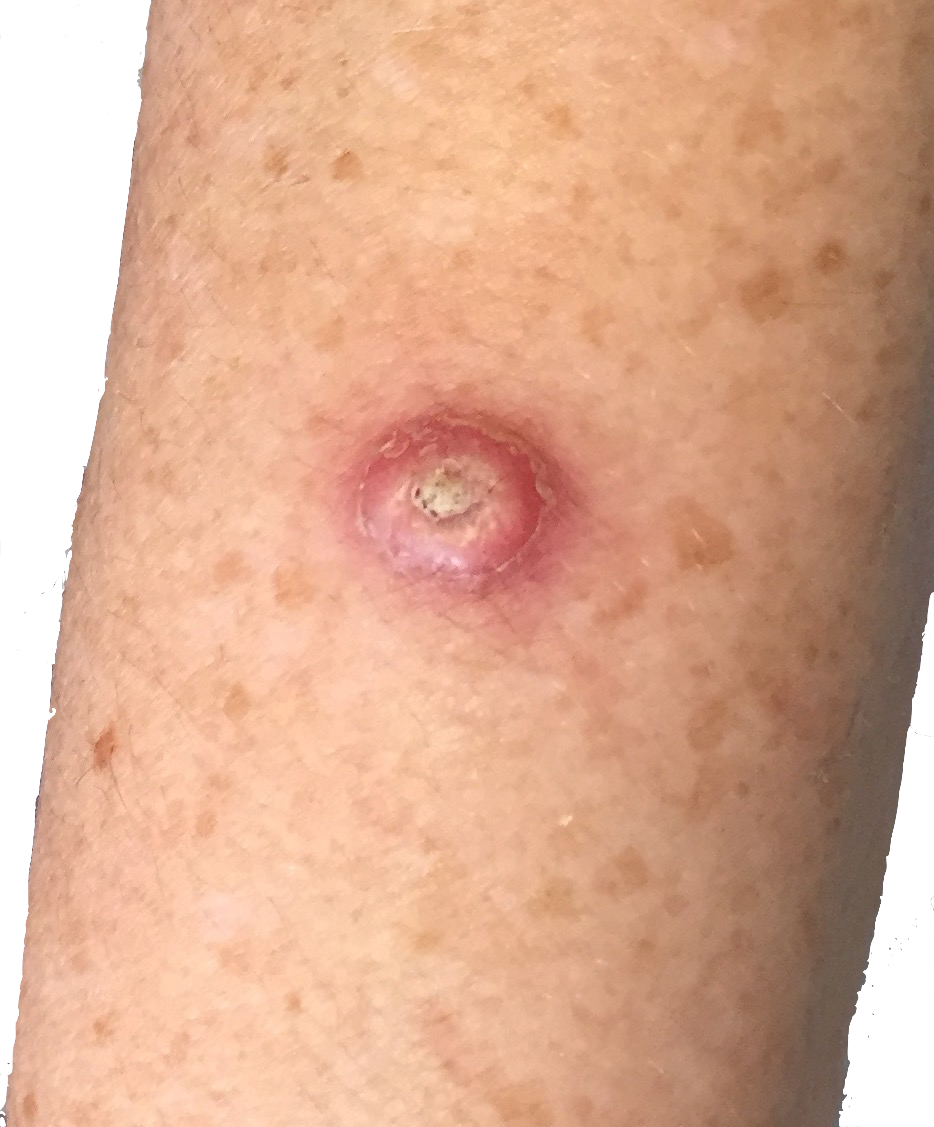
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
Squamous cell carcinoma is a skin cancer of the cells of the outer layer of the skin known as keratinocytes. The most common cause is sun exposure, although other factors can play a role such as a non-healing wound or previous trauma.
They commonly appear as a dome shaped skin coloured lump known as a nodule, which may have a plug of dry skin (keratin) in the centre or an open area in the centre (ulcer).
SQUAMOUS CELL CARcinoma on a sun exposed forearm
They do have a risk of spreading but this a low risk, on average about 5% will spread. Most are easily treated, usually by surgery, and do not cause ongoing problems.
Special sites on the body, such as the ear, scalp, nose or lip need to be treated more urgently as these are locations from which spread is more common.
SCC of the lip
This image shows a dome shaped nodule on the upper lip with a gap in the centre, known as an ulcer. A biopsy was taken to confirm that the lump was cancerous and the growth was removed with Mohs micrographic surgery. The lip was then repaired by advancing the inner lining known as the mucosa out toward the outside of the lip. The result was a normal looking lip with normal function.
a skin biopsy showing a squamous cell carcinoma
SCC of the ear
In this case, a dome shaped nodule is visible on the left earlobe. This is a high risk site for skin cancer, and also a cosmetically important site. Surgery was performed using Mohs micrographic surgery and a skin graft was placed over the area to give a normal shape and contour of the ear.
Squamous cell carcinoma treatment
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the skin is usually treated by simple skin surgery. Often, a diagnostic biopsy is performed before the surgery to confirm the diagnosis if there is any doubt or if the growth is in a high risk area such as eyelids, ears, nose, lips or scalp.
Surgical excision
Excision, which means "cutting out," is the most common method by which SCC is treated. The procedure is simple and can be performed under local anaesthetic.
Mohs micrographic surgery
This method is used when there is a need to preserve tissue at at important sites, such as eyelids, ears, noses or lips, or when there has been a recurrence of skin cancer after a previous treatment.
Skin cancer multidisciplinary team at Skin55, Harley Street.
At Skin55 we have a team of specialists that can diagnose, advise and treat squamous cell carcinoma as routine. Our skin cancer team consists of highly experienced consultants and specialist nurses who can guide you through your care.
Useful skin cancer links:
British Association of Dermatologists Squamous cell carcinoma leaflet