Benign lumps and bumps
Benign skin lesions (growths) are often referred to as “lumps and bumps.” A wide variety of these can be present on the skin, and most are amenable to treatment in expert hands. Most skin lumps are completely harmless, however some can help identify internal illnesses or genetic conditions, and others can be difficult to distinguish from more serious cancerous growths. Therefore, it is important to seek expert advice from a dermatologist regarding the nature of your skin lesion, and which is the best treatment, should any be required.
Cyst removal
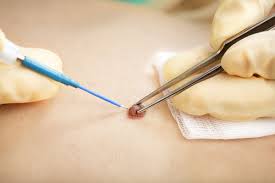
This is one of the most common operations performed in the clinic. In many areas, cyst removal is no longer available on the NHS, leading patients to opt for private healthcare for their cysts to be removed.
What is involved?
Our dermatologists specialise in removing cysts in the most aesthetic manner, with minimal scarring and inconvenience. All patients should come for an initial consultation to gain an idea of what is involved and preempt any aftercare issues.
Most patients have small or medium sized cysts (up to 1.5cm) which can be readily removed under local anesthetic. This is done by making a small incision , about 5mm in length and carefully dissecting the cyst through a small hole, with a minimally invasive technique. The wound is then stitched closed (primary closure).
Some patients with much larger or deeper cysts, several cm in size which can be treated by the same method. However, if the cyst is particularly deep or large, instead of stitching the wound closed on the day, it is packed with a dressing and allowed to heal for one or two weeks, before the final stitching of the wound (delayed or secondary closure).
Primary vs delayed / secondary closure
The advantage of stitching the wound closed right away is that there is less aftercare involved. If the wound is packed with dressings and not stitched you will need to come for regular dressing changes before the wound is actually stitched closed.
However, the disadvantage of stitching a wound at the time of operation is that blood, debris and tissue fluid collect in the space where the cyst was and become trapped under the stitches, leading to swelling, inflammation and possibly infection or leaking of the wound.
In cases of larger, deeper cysts it is best to use the delayed closure method, but with small, superficial cysts, the primary closure method is suitable.